Organic vs. Synthetic Plant Nutrition: Finding the Right Balance

In the evolving landscape of agriculture, the debate between organic and synthetic plant nutrition products continues to spark discussions among farmers, agronomists, and agricultural specialists. Understanding both approaches is crucial for making informed decisions about crop management and sustainable farming practices.
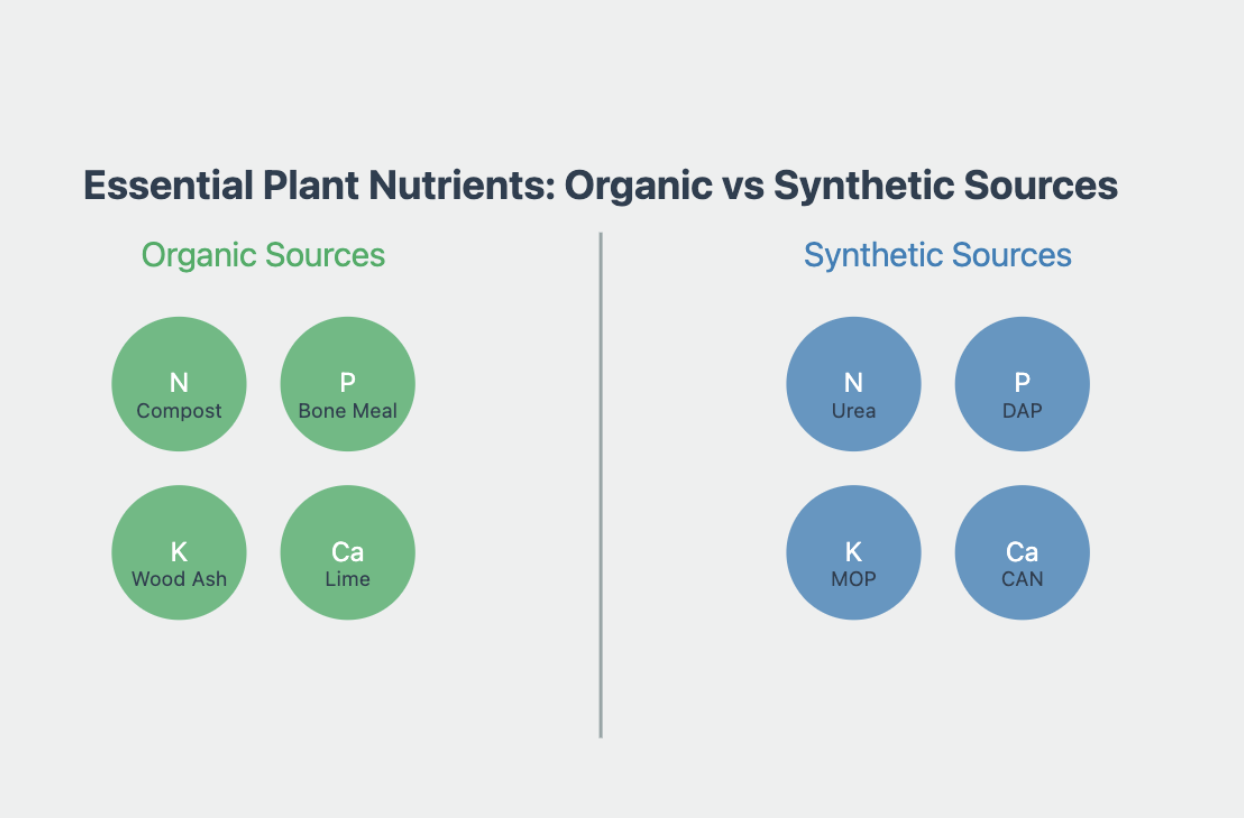
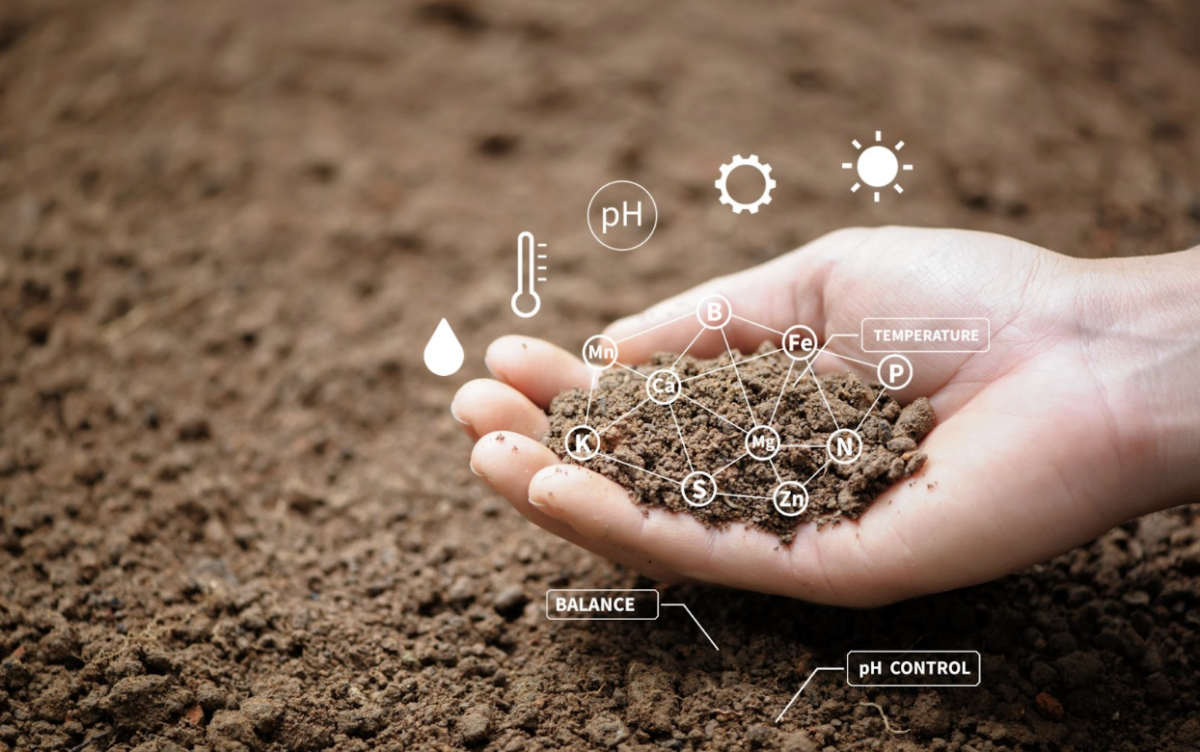
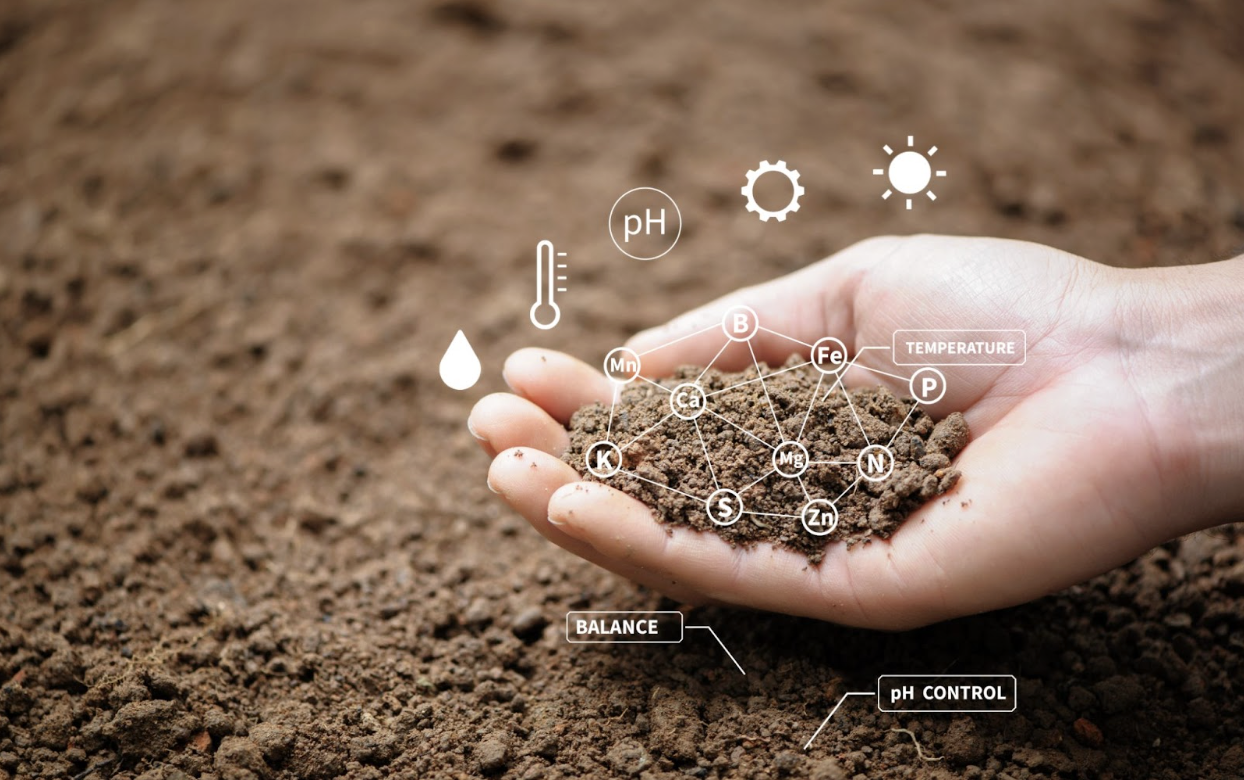
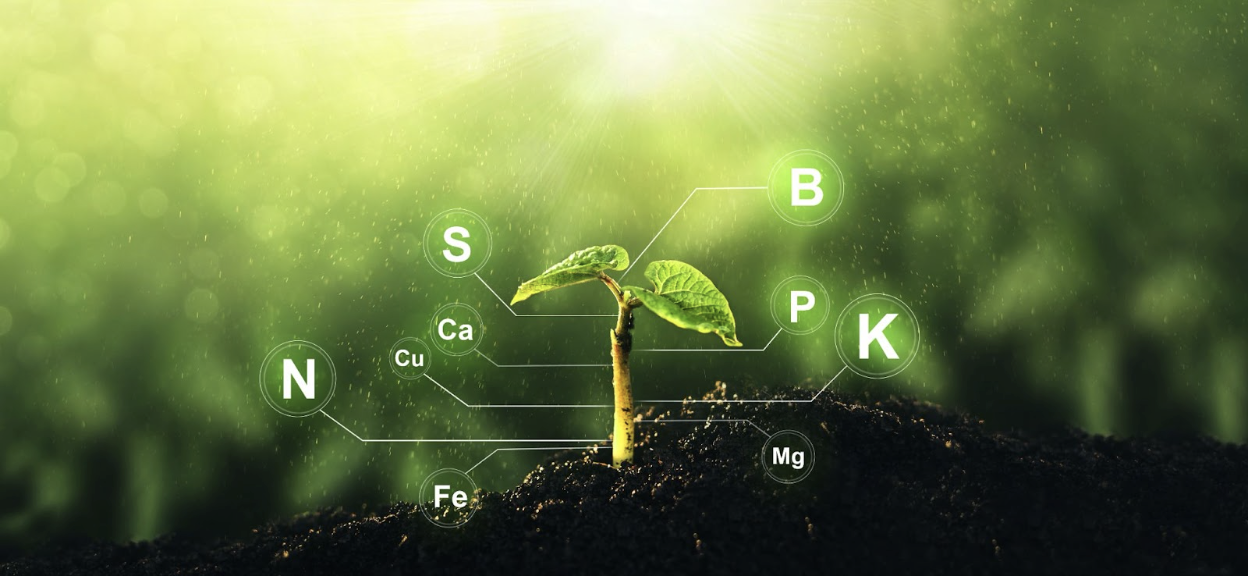
Plants require a precise balance of nutrients for optimal growth and yield. While nature provides many of these nutrients through soil organic matter and natural processes, modern agriculture often demands supplemental nutrition to meet crop demands and maintain soil fertility.
Organic Plant Nutrition Products
Organic nutrition sources offer several distinct advantages:
Natural Nutrient Release
Organic materials like compost, manure, and natural minerals release nutrients gradually, mimicking natural soil processes. This slow-release mechanism helps prevent nutrient leaching and promotes sustained plant growth.
Soil Health Benefits
Beyond providing nutrients, organic materials improve soil structure, enhance microbial activity, and increase organic matter content. These benefits contribute to long-term soil health and sustainability.
Environmental Considerations
Organic nutrition sources often have a lower environmental impact and support ecosystem services, including improved water retention and carbon sequestration.
Synthetic Plant Nutrition Products
Modern synthetic nutrition offers its own set of advantages:
Precise Nutrient Control
Synthetic fertilizers provide exact nutrient ratios, allowing farmers to address specific deficiencies quickly and effectively. This precision can be crucial during critical growth stages.
Rapid Availability
Unlike organic sources, synthetic nutrients are readily available to plants, making them ideal for addressing immediate nutrient deficiencies and supporting rapid growth phases.
Cost-Effectiveness
Synthetic products often provide more nutrients per dollar invested, making them an economical choice for large-scale operations.
Finding the Right Balance
The most effective approach often combines both organic and synthetic nutrition sources:
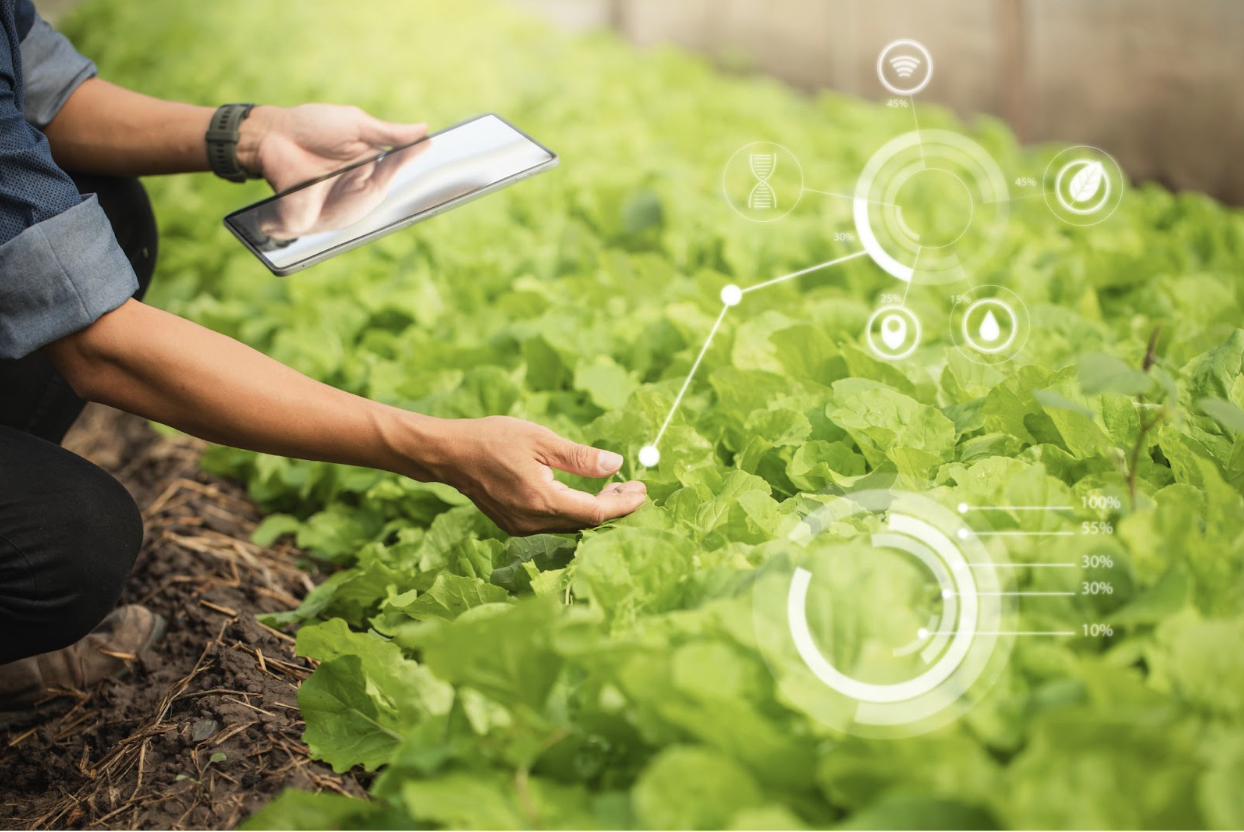
Integrated Nutrient Management

Successful farmers increasingly adopt integrated strategies that leverage the benefits of both organic and synthetic nutrition products. This approach helps:
- Maintain optimal nutrient levels
- Support soil health
- Maximize cost-effectiveness
- Ensure environmental sustainability
Timing and Application
Understanding crop requirements and timing applications appropriately ensures maximum nutrient uptake efficiency, regardless of the source.
The Future of Plant Nutrition
As agriculture continues to evolve, new technologies and products are emerging that bridge the gap between organic and synthetic nutrition. These innovations focus on:
- Enhanced efficiency fertilizers
- Biostimulants and biological products
- Precision application technologies
- Sustainable nutrient management practices
Conclusion
The choice between organic and synthetic plant nutrition products isn’t necessarily an either-or decision. Success lies in understanding crop needs, soil conditions, and environmental factors to create a balanced nutrition program that optimizes both yield and sustainability.